At HANSAmed, we recognize the critical importance of treating and eliminating infections like periodontitis from one's body due to its significant correlation with other systemic diseases.
-
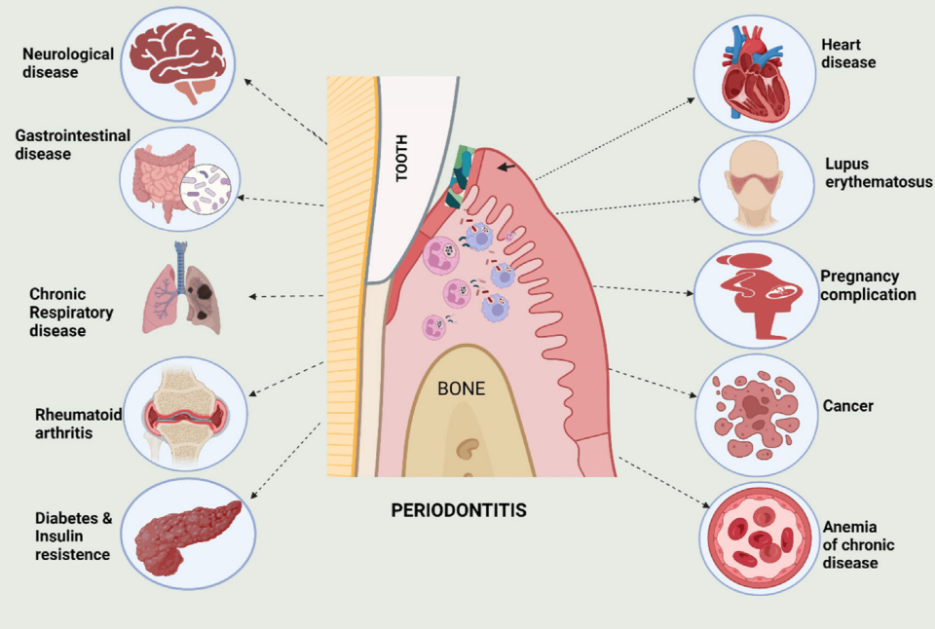
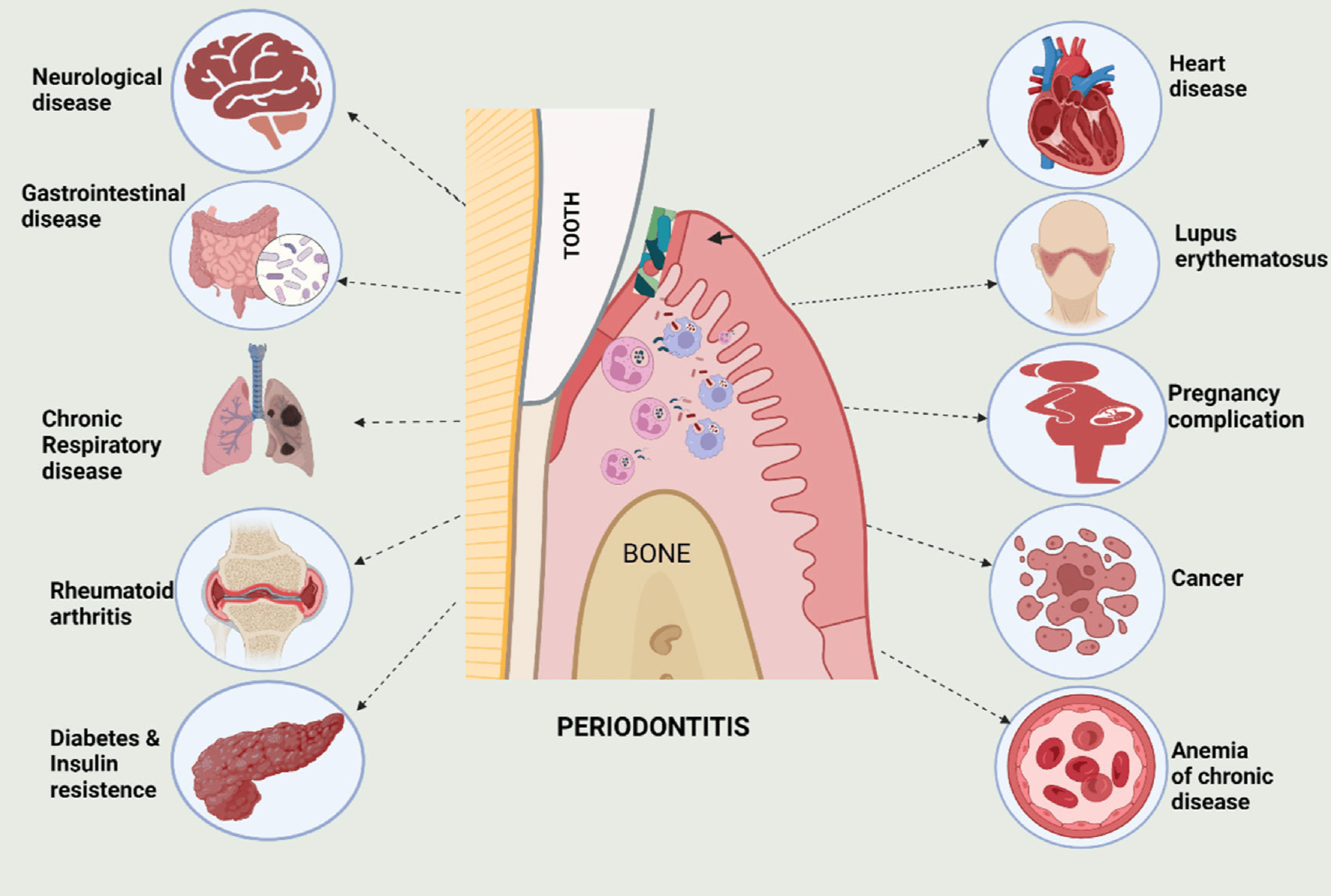
Effects of Periodontitis on Major Organ Systems
Drishti V Lohiya, Ashok M Mehendale, Divya V Lohiya, Harsh S Lahoti, and Vidhi N Agrawal. 2023
This study explores the systemic impacts of periodontitis, a chronic inflammatory condition of the gums. The research underscores the far-reaching consequences of periodontal disease beyond oral health, affecting multiple major organ systems through various mechanisms.
|
Cardiovascular System Periodontitis has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and stroke. The inflammatory process in the gums can lead to the release of bacterial endotoxins and inflammatory mediators into the bloodstream, contributing to vascular inflammation and plaque formation in the arteries. |
|
Respiratory System Oral bacteria from periodontitis can be aspirated into the lower respiratory tract, potentially leading to respiratory infections like pneumonia. This is particularly concerning for individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other pre-existing respiratory conditions.
|
|
Renal System Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has also been associated with periodontitis. The systemic inflammation and bacterial dissemination from the oral cavity can exacerbate renal inflammation and dysfunction, further complicating the health of patients with CKD. |
|
Endocrine System Diabetes mellitus and periodontitis share a bidirectional relationship. Periodontitis can worsen glycemic control in diabetic patients, while poorly controlled diabetes can exacerbate periodontal disease due to impaired immune response and increased susceptibility to infections. |
|
Reproductive System Emerging evidence suggests that periodontitis may adversely affect reproductive health, including adverse pregnancy outcomes like preterm birth and low birth weight. The underlying mechanism involves systemic inflammation and the potential translocation of periodontal pathogens to the placenta. |
|
Immune System Periodontitis can lead to a persistent low-grade systemic inflammatory state, which can modulate immune function and increase susceptibility to other inflammatory conditions and infections. |
The study emphasizes the importance of maintaining oral health not only for preventing local oral diseases but also for protecting overall systemic health. Regular dental check-ups and effective periodontal treatments are critical for mitigating the systemic risks associated with periodontitis.
>> Click to access the article <<
Related studies: